Petrosal nerve (a nerve traveling through the petrous portion of the temporal bone) may refer to:
- Deep petrosal nerve
- Greater petrosal nerve (also known as the greater superficial petrosal nerve)
- Lesser petrosal nerve (also known as the lesser superficial petrosal nerve)
- External superficial petrosal nerve
Deep petrosal nerve:
The deep petrosal nerve (n. petrosus profundus; large deep petrosal nerve) is given off from the carotid plexus, and runs through the carotid canal lateral to the internal carotid artery.
It contains postganglionic sympathetic fibers with cell bodies located in superior cervical ganglion.
It then enters the cartilaginous substance which fills the foramen lacerum, and joins with the greater superficial petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal(Vidian nerve).
Then pass through the pterygopalatine ganglion without synapsing, and then join the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in supplying the lacrimal gland & nasal and oral mucosa.
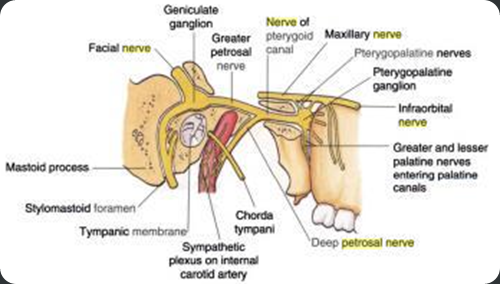
Greater petrosal nerve : The greater superficial petrosal nerve (n. petrosus superficialis major; large superficial petrosal nerve) is given off from the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve; it passes through the hiatus of the facial canal, enters the cranial cavity, and runs forward beneath the dura mater in a groove on the anterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. It then enters the cartilaginous substance which fills the foramen lacerum, and joining with the deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal.

Vidian nerve : The nerve of the pterygoid canal (n. canalis pterygoidei [Vidii]; Vidian nerve), formed by the junction of the two preceding nerves in the cartilaginous substance which fills the foramen lacerum, passes forward, through the pterygoid canal, with the corresponding artery, and is joined by a small ascending sphenoidal branch from the otic ganglion. Finally, it enters the pterygopalatine fossa, and joins the posterior angle of the sphenopalatine ganglion.


The geniculate ganglion is formed by the juncture of the nervus intermedius and the facial nerve into a common trunk. Additional afferent fibers from the anterior two thirds of the tongue are added to the geniculate ganglion from the chorda tympani.
Three nerves branch from the geniculate ganglion:
- the greater superficial petrosal nerve,
- the lesser petrosal nerve, and
- the external petrosal nerve.

Lesser petrosal nerve :
- The lesser petrosal nerve carries parasympathetic (secretory) fibers from both the tympanic plexus (from glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) via Jacobson's nerve) and the nervus intermedius, to the parotid gland.
- It originates at the geniculate ganglion, passing forwards through its own canal back into the middle cranial fossa.
- Here it is between the two layers of the dura mater, passing forwards to exit the skull via foramen ovale to eventually join the otic ganglion.
External superficial petrosal nerve:
- The external petrosal nerve is an inconstant branch that carries sympathetic fibers to the middle meningeal artery.